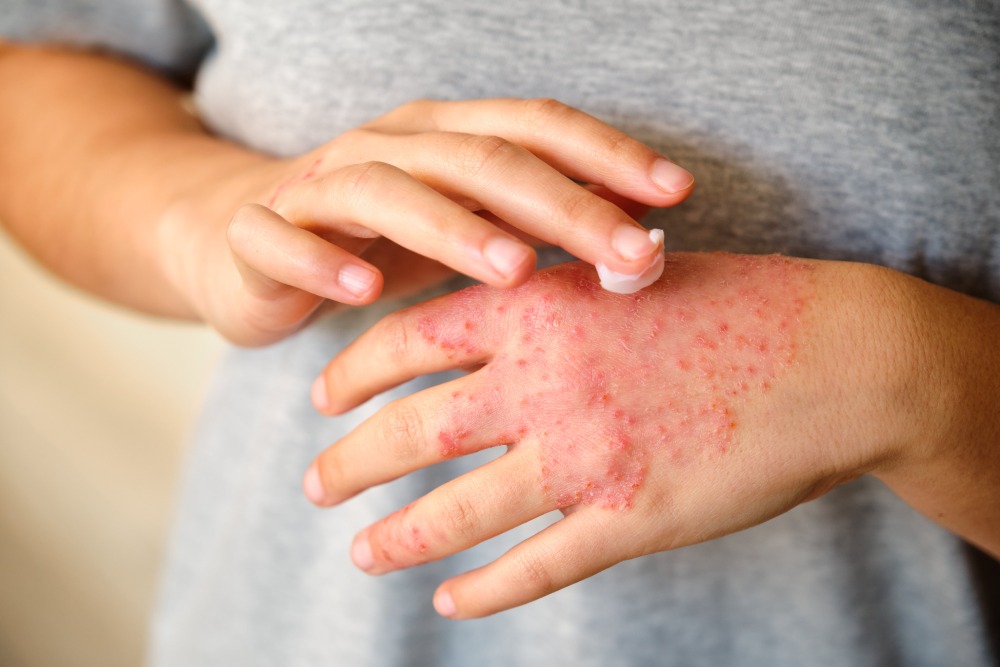
Eczema, a common skin condition, can be particularly challenging when it affects visible areas like the face and hands.
At PharmaChoice, we understand the impact this can have on your daily life and self-esteem.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore effective strategies for managing eczema, ensuring you receive the most current and reliable information.
What Is Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)?
Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, is an inflammatory skin condition characterized by dry, itchy skin. It’s a chronic issue that affects both children and adults, with varying degrees of severity.
According to the Mayo Clinic, eczema is more common in children, but it can continue into adulthood or even start later in life.
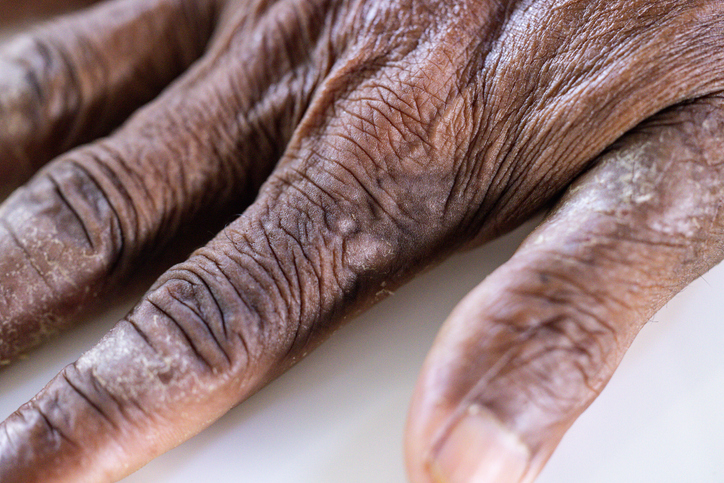

Common Eczema Types
Eczema, a term encompassing various types of skin conditions, manifests in different forms, each with unique characteristics and triggers.
Understanding these types can help identify and manage the condition more effectively.
Atopic Dermatitis:
This is the most common form of eczema, often beginning in childhood.
Atopic dermatitis is part of the “atopic triad,” which also includes allergies and asthma, indicating a common genetic background.
Those with atopic dermatitis typically have a family history of these conditions.
The skin becomes dry, itchy, and inflamed, often appearing on the face, neck, and the insides of the elbows, knees, and ankles.
It’s a chronic condition that tends to flare periodically and then subside. Managing atopic dermatitis involves moisturizing the skin, avoiding triggers, and using prescribed medications to reduce inflammation and itching.
Contact Dermatitis and Allergic Dermatitis:
Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin comes into contact with an irritant or allergen, leading to an allergic reaction. Irritants can be everyday substances like soaps, detergents, or even certain fabrics.
Allergic contact dermatitis, on the other hand, is caused by a reaction to substances such as nickel, fragrances, or poison ivy.
The skin in contact dermatitis typically becomes red, itchy, and inflamed, and may develop blisters. Identifying and avoiding the triggering substance is key to managing this type of eczema.
Nummular Dermatitis:
Also known as discoid eczema, nummular dermatitis is characterized by distinct, coin-shaped spots or patches on the skin.
These patches can be itchy and scaly and sometimes ooze fluid. The exact cause of nummular dermatitis is unknown, but it can be triggered by skin injuries, such as a bug bite or a burn.
It’s more common in older adults and can be exacerbated by dry skin. Treatment typically involves moisturizing the skin, applying topical steroids to reduce inflammation, and avoiding irritants.
Dyshidrotic Dermatitis:
This type of eczema is specific to the hands and feet, characterized by small, itchy blisters on the palms, sides of the fingers, and soles of the feet.
The cause of dyshidrotic dermatitis is unknown, but it’s thought to be related to seasonal allergies or stress.
It can also be more common in people who have their hands in water frequently or are exposed to metal salts like cobalt and nickel.
Managing dyshidrotic dermatitis involves avoiding triggers, using hand creams, and in some cases, applying steroid creams to reduce inflammation.
Each type of eczema has its unique challenges and management strategies.
If you suspect you have any form of eczema, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan.
At PharmaChoice, our pharmacists are equipped to provide expert advice and support for managing these various types of eczema.
What Causes Eczema Flare-Up?
Eczema flare-ups can be triggered by various factors:
- Irritants: Everyday products like soaps and detergents can aggravate eczema.
- Allergens: Pollen, pet dander, and dust mites are common culprits.
- Stress: Emotional stress can worsen symptoms.
- Foods: Certain foods may trigger eczema in some people.
- Clothing: Rough or tight-fitting clothing or certain fabrics can irritate the skin.
Who Can Get Eczema?
Eczema, a prevalent skin condition, does not discriminate by age, affecting both children and adults, albeit often in different forms.
In fact, The Canadian Skin Patient Alliance explains Atopic Dermatitis is one of the world’s most common skin conditions, with 10-15 percent of children under five affected, 40 percent of which will live with it throughout adulthood.
Understanding these variations can be crucial for effective management and treatment.
Eczema in Adults
In adults, eczema typically manifests as dry, scaly patches of skin. These patches are often itchy and can appear anywhere on the body, but they are commonly found on the neck, face, and the bends of elbows and knees.
The chronic nature of the condition means that adults might experience periods of flare-ups followed by times of remission.
Stress, environmental factors, and skin irritants are common triggers for adult eczema.
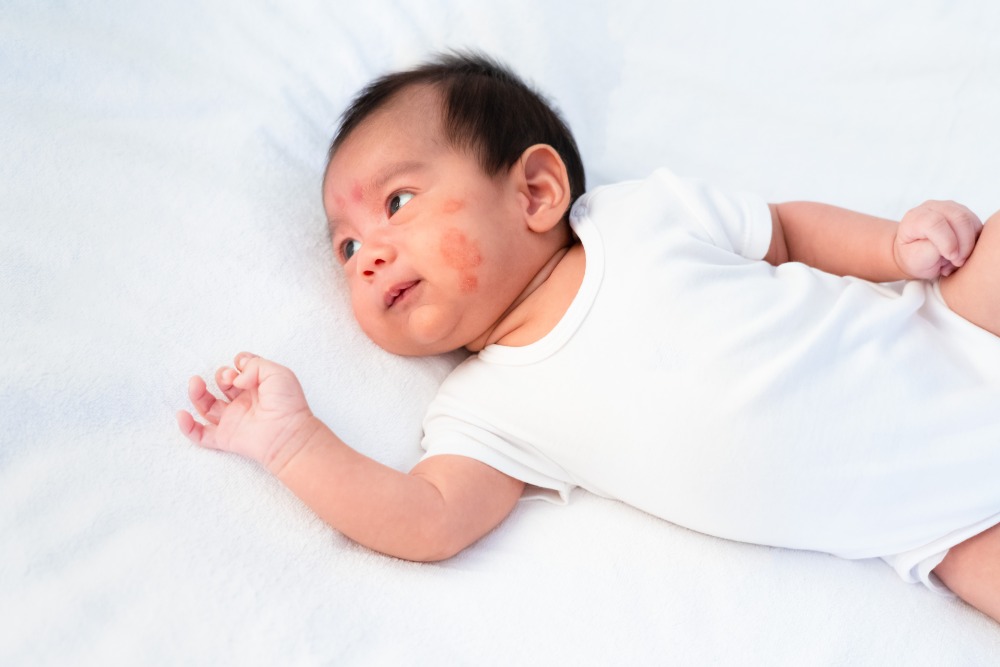
Eczema in Children
For children, eczema often presents differently. It may appear as red, crusted, or weeping spots.
In infants, eczema frequently occurs on the face, especially the cheeks and chin, but it can also spread to other parts of the body.
As children grow, eczema tends to localize in the bends of elbows and knees, similar to adults.
It’s important to note that children with eczema might be more prone to skin infections due to itching and scratching, which can break the skin.
Regardless of age, managing eczema involves a combination of skincare routines, avoiding known triggers, and possibly medication to control itching and inflammation.

Most Common Eczema Symptoms
Understanding the symptoms of eczema is crucial for early detection and effective management. Here are the most common signs to look out for:
Discoloured Skin:
One of the primary indicators of eczema is changes in skin colour. Affected areas may appear redder, darker, or even lighter than the surrounding skin.
As explained by the Eczema Society of Canada, this discoloration often varies based on skin colour. Furthermore, the severity of the discoloration can also vary depending on the stage of the eczema.
It’s important to note that while the discoloration can improve with treatment, it may take some time to return to the skin’s natural tone.
Dry Patches of Skin:
Eczema commonly causes areas of dry, rough, and flaky skin. The dryness is due to a compromised skin barrier, which fails to retain moisture effectively.
Regular application of moisturizers is essential to help manage this dryness.
Look for products specifically formulated for sensitive and eczema-prone skin to provide the necessary hydration without causing irritation.
Thickened Skin:
Chronic scratching or rubbing of itchy eczema patches can lead to skin thickening, a condition known as lichenification.
This thickening is the skin’s response to repeated irritation and can create a leathery texture. Thickened skin may also develop deeper lines and take on a more pronounced appearance.
It’s important to address the underlying itch and inflammation to prevent or reduce skin thickening.
In some cases, your healthcare provider may recommend specific treatments to soften the thickened skin and alleviate symptoms.
Itching:
Perhaps the most distressing symptom of eczema is persistent itching. Itching can range from mild to severe and often worsens at night, affecting sleep quality.
The itch-scratch cycle can exacerbate the condition, leading to more inflammation and even skin infections if the skin is broken.
To manage itching, keep the skin moisturized, use anti-itch creams or lotions as recommended, and avoid triggers known to exacerbate your eczema.
In some cases, oral medications or light therapy may be prescribed to help control severe itching.
Recognizing these symptoms is the first step in managing eczema effectively.
Eczema Treatment – How Is Eczema Treated?
Effective eczema management requires a personalized approach, taking into account the specific area affected and the individual’s unique needs.
Here are some tailored strategies for different areas of the body:
How To Treat Eczema On Face
Facial eczema demands a gentle approach due to the sensitivity of facial skin. It’s crucial to use hypoallergenic and non-comedogenic products that won’t clog pores or exacerbate symptoms.
Non-steroid moisturizers like Cerave or our Option+ moisturizing creams can also provide relief by hydrating and protecting the skin barrier.
Avoid products containing fragrances, alcohol, or harsh chemicals, as these can irritate the delicate facial skin. In some cases, a mild topical corticosteroid may be prescribed for short-term use to reduce severe inflammation.
How To Treat Eczema On Hands
Hand eczema can be particularly challenging due to frequent washing and exposure to irritants.
Protect your hands by wearing gloves when using cleaning agents or doing tasks that may expose your skin to irritants.
Regularly apply a thick, barrier-forming moisturizer to keep the skin hydrated. Medicated creams like Clobetasol cream can be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider to reduce inflammation and itching.
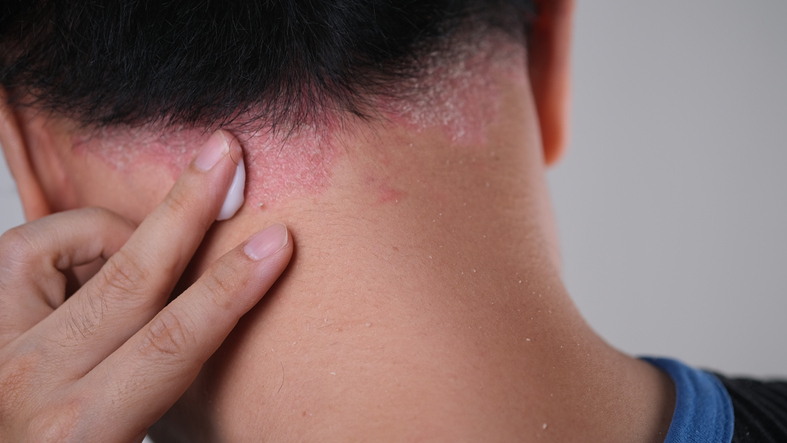
How To Treat Eczema On Scalp
Scalp eczema can be treated with a gentle, medicated shampoo designed to soothe the scalp and reduce flakiness.
Eucrisa, a non-steroidal topical medication, can also be used for scalp eczema. However, steroid scalp lotions such as Betaderm scalp lotion are medicated options, and they are designed specifically to treat the scalp.
Avoid products with fragrances, and try not to scratch the scalp, as this can worsen the condition.
How To Treat Eczema Around Eyes
The skin around the eyes is extremely delicate, making eczema in this area challenging to treat. Use only mild, fragrance-free products, and be cautious with any topical treatments.
Due to the sensitivity of the area, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before applying any medication.
They may prescribe low-potency topical steroids or non-steroidal treatments.
How To Treat Eczema Bumps
Eczema bumps, or papules, can be treated with topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and itching.
These should be used as directed by a healthcare provider, as overuse can lead to skin thinning or other side effects.
Moisturizing regularly with a thick cream or ointment can also help soothe the skin and prevent new bumps from forming.
How To Treat Baby Eczema
Baby eczema requires gentle care. Use fragrance-free, hypoallergenic products designed for sensitive skin.
Moisturize your baby’s skin several times a day with a thick, fragrance-free cream or ointment. Avoid using harsh soaps or bubble baths and opt for mild, fragrance-free cleansers.
Dress your baby in soft, breathable fabrics and avoid wool or other scratchy materials.
In all cases, it’s important to identify and avoid potential triggers, keep the skin well-moisturized, and consult with healthcare professionals for personalized treatment plans.
Recommended Eczema Creams
Topical corticosteroids are a mainstay in eczema treatment. These creams and ointments are effective in reducing inflammation, itching, and redness associated with eczema.
One commonly prescribed corticosteroid is Betaderm, known for its efficacy in managing mild to moderate eczema flare-ups and its various forms.
It’s crucial, however, to use these steroids as directed by a healthcare provider, as overuse or incorrect application can lead to side effects such as skin thinning or increased vulnerability to infections.
In addition to corticosteroids, there are other types of creams and ointments specifically designed for eczema-prone skin.
For mild eczema, over-the-counter hydrocortisone creams can be effective. However, they should be used with caution and only for short-term relief.
Eczema Prevention Tips
Preventing eczema flare-ups is a crucial part of managing the condition. Here are some effective strategies:
- Keeping Skin Clean:
Maintaining clean skin is essential in preventing eczema flare-ups. Use gentle, fragrance-free cleansers that don’t strip the skin of its natural oils.
It’s also advisable to pat the skin dry gently after washing, rather than rubbing, to avoid irritation.
- Avoiding Hot Showers:
While a hot shower can feel relaxing, it can be detrimental to eczema-prone skin. Hot water can strip away natural oils, leading to dryness and irritation.
Opt for lukewarm water instead, and try to keep showers short – ideally, no longer than 10-15 minutes.
- Keeping Skin Moisturized:
Regular application of moisturizers is key in managing eczema. Moisturizers help to maintain the skin’s barrier function and prevent dryness.
Apply moisturizer immediately after bathing and throughout the day as needed, especially during colder, drier months.
- Avoiding Itching:
Itching is a common and troublesome symptom of eczema, but scratching can damage the skin and lead to worsening of the condition.
To help alleviate itching, keep the skin moisturized, use anti-itch creams as recommended by your healthcare provider, and wear soft, breathable clothing.
By incorporating these tips into your daily routine, you can effectively reduce the frequency of eczema flare-ups and improve your skin health.
Remember, managing eczema is an ongoing process, and what works for one person may not work for another.
Eczema Home Remedies
Some natural remedies include:
- Oils: Coconut or sunflower seed oil can soothe the skin.
- Tea: Green tea has anti-inflammatory properties.
- Acupuncture and Aromatherapy: These can help with stress management.
- Relaxation techniques: Yoga and meditation can reduce stress-related flare-ups.
When Should I See My Healthcare Provider?
Eczema can often be managed effectively with over-the-counter treatments and home care strategies.
However, there are certain situations where it’s crucial to seek professional medical advice.
Understanding when to consult your healthcare provider can help in better managing the condition and preventing complications.
- Eczema Symptoms Worsen or Don’t Respond to Treatment:
If you notice that your eczema symptoms are getting worse despite using over-the-counter creams and following self-care measures, it’s time to see a healthcare provider.
This includes increased redness, swelling, or itching that becomes unbearable.
- Interference with Sleep or Daily Activities:
Eczema can be more than just a skin condition; it can significantly impact your quality of life.
If you find that the itching and discomfort caused by eczema are disrupting your sleep or making daily tasks difficult, seek medical advice.
- Development of a Fever or Infection:
One of the risks of eczema, especially with excessive scratching, is the development of skin infections.
If you notice signs of infection, such as increased pain, redness, warmth, or swelling, or if you develop a fever, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
Eczema FAQs
How is eczema diagnosed?
Eczema is diagnosed based on a physical examination and medical history. Sometimes, allergy tests are conducted.
How can eczema be cured?
There’s no cure for eczema, but symptoms can be managed effectively.
Psoriasis vs eczema – How do I know if it’s eczema or psoriasis?
Psoriasis usually has thicker, more defined scales than eczema. A healthcare provider can provide a definitive diagnosis.

Ease The Symptoms of Eczema Today – Talk to Your PharmaChoice Pharmacist
While eczema can be a challenging condition, effective management is possible. Remember, each case is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another.
We at PharmaChoice are committed to helping you find the right treatment and support.
Visit your closest PharmaChoice pharmacy and consult with our pharmacists for personalized advice and treatment options. Let us help you manage your eczema and live your best life.